Causes, Symptoms and Treatments Ectopic Pregnancy and Infertility in Anand
Ectopic pregnancy is the most common cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester. The implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity is known as ectopic pregnancy. The fertilized egg passes from the fallopian tube into the uterus, where the pregnancy develops, into a normal pregnancy. However, in a tiny number of pregnancies, the embryo implants outside the uterus, resulting in an ectopic pregnancy. The fallopian tube is where the majority of extrauterine pregnancies (97%) implant; the cervix, ovary, peritoneal cavity, and uterine scars are where the remaining 3% of ectopic pregnancies implant. As the pregnancy progresses into an ectopic pregnancy, the tube might burst, resulting in internal bleeding. This is a life-threatening scenario that requires immediate medical attention.
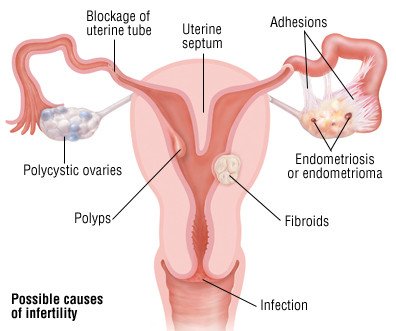
Ectopic pregnancy is connected to a range of risk factors, including pelvic inflammatory disease, intrauterine devices, tubal operations, sexually transmitted illnesses, and infertility.
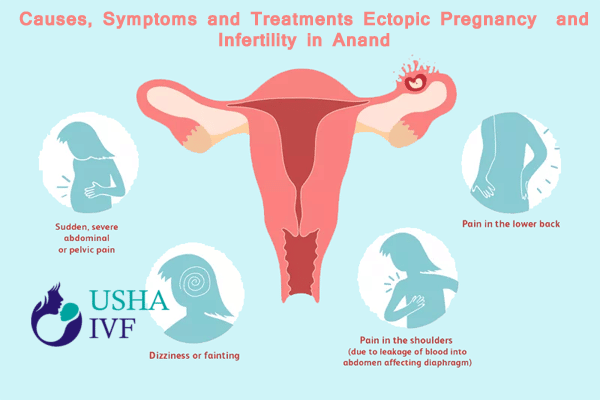
Ectopic pregnancy affects around 0.25-2.0 percent of all pregnancies worldwide* and can affect any sexually active woman of reproductive age. In Usha IVF IVF and Fertility Treatment center in Anand, Gujarat, India, ectopic pregnancy was observed in 0.91 percent of pregnant women (with no maternal fatalities).
Globally the incidence of ectopic pregnancy has been on the rise over the past few decades because of increased incidence of salpingitis (infection of fallopian tubes mostly due to sexually transmitted infections), induction of ovulation, and tubal surgeries; and improved ability to detect ectopic pregnancy. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy has risen from 4.5 cases per 1,000 pregnancies in 1970 to 19.7 cases per 1,000 pregnancies in 1992 in North America. Though the cases of ectopic pregnancy are on rising; the incidence of rupture of ectopic pregnancy and maternal deaths has declined because of early diagnosis and management. Ectopic pregnancy still accounts for 4% to 10% of pregnancy-related deaths and leads to a high incidence of ectopic site gestations in subsequent pregnancies.